NVIDIA is well-known company all over the world which designs the graphics processing units (GPUs) for the gaming market, as well as system on a chit units (SOCs) for the mobile computing and automotive market. GPU-accelerated computing is the use of a graphics processing unit (GPU) together with a CPU to accelerate scientific, analytics, engineering, consumer, and enterprise applications. You are here most probably because you are a Linux user and you may have faced difficulties in past while installing GPU drivers, sometimes it is really difficult to configure manufacturer drivers for NVIDIA cards in Linux, there could be many reasons for this such as kernel upgrade, dependencies issue and so. By default Ubuntu use the open source video driver Nouveau for NVIDIA graphics card. This driver lacks support for 3D acceleration and may not work with the very latest video cards or technologies from NVIDIA. A proprietay alternative to Nouveau are the closed source unified NVIDIA drivers, which are developed by NVIDIA. This driver provides excellent 3D acceleration and video card support.

Release Highlights of 367.27 Drivers for Linux:
- Added support for VDPAU Feature Set H to the NVIDIA VDPAU driver. GPUs with VDPAU Feature Set H are capable of hardware-accelerated decoding of 8192×8192 (8k) H.265/HEVC video streams.
- Fixed a bug that caused the X server to sometimes skip displaying Vulkan frames when the Composite extension is enabled.
- Fixed a bug that would cause OpenGL applications to crash when creating a context on one X display connection, then making it current with no associated drawable on another X display connection. This fixes a crash when starting some versions of Matlab.
- Fixed OpenGL presentation to SDI through the GLX_NV_video_out and GLX_NV_present_video extensions, which was broken by the introduction of the nvidia-modeset kernel module in 358.09.
- Fixed a bug that caused an incorrect offset to be applied when using the full composition pipeline on a display whose image has both a rotation and a ViewportOut offset applied.
- Fixed a bug that could cause nvidia-settings to crash on some systems when responding to events such as hotplugging DisplayPort devices.
- Fixed a bug that could cause crashes in OpenGL applications which use glTextureView() with a non-zero minlevel.
- Enhanced the Display Device information page in nvidia-settings with additional information for DisplayPort devices to reflect attributes which are specific to DisplayPort connections.
- Fixed a bug which could cause deleted application profiles to appear when editing rules in the nvidia-settings control panel.
- Fixed a bug that caused hangs when a G-SYNC monitor is unplugged and a non-G-SYNC monitor is connected while G-SYNC is active.
- Fixed a bug that caused “nvidia-modeset: ERROR: GPU:0: Activating G-SYNC failed” to be printed to the system log if a G-SYNC monitor is connected and stereo is enabled in xorg.conf on a configuration that doesn’t support it.
- Added the NV_robustness_video_memory_purge OpenGL extension, which
- allows applications to know when a mode switching or power event purged the contents of FBOs and BOs residing in video memory.
- Fixed a bug that prevented HDMI 2.0 4K monitors from waking up from sleep or hot-replug.
- Fixed a bug that could lead to a system crash if there was a peer-to-peer mapping still active during CUDA context teardown.
So there are two ways to install Nvidia drivers using the Ubuntu community PPA and make sure to read information on PPA page before you proceed to installation process. Run the following two commands in the terminal then follow any method to install Nvidia drivers in your system.
Available for Ubuntu 16.04 Xenial/15.10 Wily/14.04 Trusty/12.04 Precise/Linux Mint 18/17/13/other related Ubuntu derivatives
Install Nvidia Drivers in Ubuntu/Linux Mint open terminal (Press Ctrl+Alt+T) and enter following commands:
1st Method:
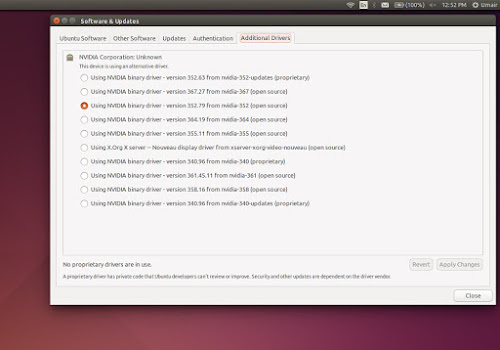
Once you ran the commands, open “Additional drivers” and select drivers you want to install for Nvidia GPU.
2nd Method:
You can install any driver using any of these commands, make sure to not run all of them, choose only one command that suits your GPU.
Install Nvidia Drivers in Ubuntu/Linux Mint open terminal (Press Ctrl+Alt+T) and enter following commands:
Version 367.27 – For Ubuntu 16.04/15.10/14.04/12.04/Linux Mint 18/17/13
 Linus Torvalds has announced the release of a Linux 4.14, the latest stable release of the Linux kernel.
Linus Torvalds has announced the release of a Linux 4.14, the latest stable release of the Linux kernel.




Je moet ingelogd zijn om een reactie te plaatsen.